Welcome to the first of an undefined number of posts focusing on sustainable investing, specifically ESG investing. Over the course of the series I’ll be taking you through the fundamentals of sustainable and ESG investing, how it can be implemented by individuals, the impact ESG investing might have on expected returns and it’s shortcomings, reviewing existing studies on ESG investing, and finally drawing conclusions from my own research (with some help from friends). This is going to be a unique process because it will be a constant work in progress…
In the past, I’ve never been in a position as a financial advisor to implement ESG investing in clients’ portfolios, so I never spent much time really researching the philosophy; I knew what it was, but that was about it. Now that I own my firm, things have changed. There is no question interest in ESG investing is growing, this trend will only continue with Millennials beginning to make their impact on the investment community; they are entering the phase in their life when they begin planning for their futures and paying attention to investing. I can attest to this as Millennials are the fastest growing, in terms of numbers, segment of my business. As we will discuss shortly, Millennials are interested in aligning their investments with their values, so it makes sense for me to take a closer look at ESG investing. In addition to the business aspect of the research, I am personally interested to find out if ESG investing will allow me the opportunity to have my cake and eat it too.
By the end of this series I hope you, the reader, will have learned about a new way to look at investing that may align better with your personal beliefs, and I, the advisor, will have determined whether or not ESG investing is a strategy I will implement with clients.
Without any further ado, let’s dive into the basics today…
Sustainable Investing
Before we get into ESG investing, we need to start with the category of investing it falls under, SRI investing. According to US SIF, The Forum for Sustainable and Responsible Investment, “Sustainable, responsible, and impact investing (SRI) is an investment discipline that considers environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term competitive financial returns and positive societal impact.”1 In other words, SRI investing is an investment philosophy that focuses not only on investment growth, but also on making a positive impact.
There are different approaches to SRI investing:
I. Exclusionary Screening
- Excluding companies that do not adhere to the investment mission, or beliefs.
- Examples: Tobacco companies, Firearms companies, Alcohol companies
II. Impact Investing
- Investing in companies with the intention to generate measurable social, or environmental impact.
- Examples: Green companies, Companies providing health coverage to impoverished countries (Note: These often are private investments), Social Impact Bonds
III. ESG Investing
- Investing in companies scoring positive using criteria to evaluate their impact on the environment, social issues and corporate governance. Investments are made in companies with high ESG scores.
- Examples: Best-in-class ESG scores, Low carbon footprint, Use of green technologies
Our focus for this post, and the ones to follow, is ESG investing.
ESG Investing
Just in case you missed it earlier, the criteria evaluated in ESG investing are Environment, Social and Corporate Governance. Investors evaluate and rank companies according to their impact in the ESG areas, ranking those with positive impacts high, and those with negative impacts as low. To give you a current example, let’s look at the United Airlines fiasco. Due to the treatment of the passenger removed from the plane, the CEO’s response in the media, and a couple of other recent incidents involving UAL, it would would receive a low ranking for corporate governance. Depending on the focus of the ESG investment strategy, UAL may not make the cut.
Some broader examples are :
Environment
- Carbon footprint
- Waste production
- Packaging
- Use of clean technology
- Green companies
Social
- Gender equality
- Management practices
- Health and safety of workers
- Labor practices of suppliers
Corporate Governance
- Executive compensation (compared to peers)
- Shareholder rights and protection
- How well the company manages itself
- Any past corrupt practices
In implementing an ESG investment strategy, it is up to the individual investor, or asset manager to determine the specific criteria to be used, the ranking system, and which stocks to include in the investment strategy. The criteria can be as broad as best-in-class amongst the ESG categories, or focusing on a specific category like environmental impact. The beauty of an ESG investment philosophy is it allows the investor to customize the screens to capture their beliefs; whether or not being too restrictive with the ESG criteria is good for returns is yet to be addressed in my research. We will see.
An important difference between ESG investing and exclusionary screening, the other common SRI approach, is ESG investing takes a proactive approach to include companies with high ESG rankings. This leads to the investor allocating towards companies truly in line with their beliefs, rather than not allocating towards companies with practices against their beliefs. Those may seem like two roads leading to the same end point, but they’re not. ESG investing gives the investor the opportunity to support, and therefore impact companies they believe in; it is a direct impact. Exclusionary screening just makes sure their money doesn’t go to causes they don’t support. It may seem like a minor difference, but for investors interested in ESG investing, directing their money to companies they support is important.
Why is ESG Investing Gaining Popularity?
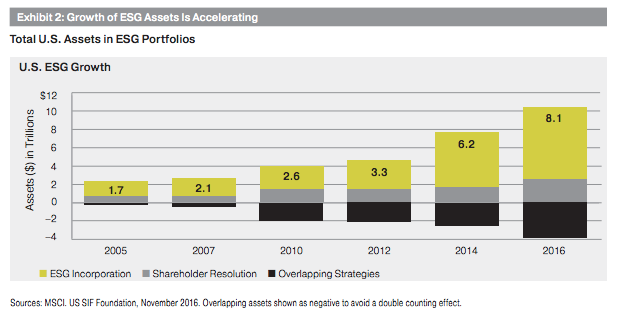
Quite simply, ESG investing is becoming more popular because of Millennials.
According to a 2015 TIAA survey, 90% of affluent Millennials said they were interested in not only realizing competitive investment returns, but promoting positive social and environmental outcomes; this compared to only 76% of affluent non-Millennials2 . This was supported by an OppenheimerFunds and Campden Research survey that found 84% of ultra-high-net worth Millennials were interested in socially responsible investing2 . While most Millennials would not consider themselves affluent, or ultra-high-net worth, that does not mean they do not share the same focus. According to an American Century Investment study, 54% of Millennials consider the social impact of their investments as an important factor in their decision making process; this compares to 34% of Generation X and 37% of Baby Boomers3.
The Millennials, my generation, are more aware of our impact on society and the environment, and we are focused on improving the world and leaving it in better shape for our children. This may have earned us a reputation of being sensitive, soft, or naive, but at the end of the day we will be in control of the dollars being invested, and companies with good ESG scoring will be rewarded.
Millennials are the most educated generation to date; Millennials are interested in gender and social equality; Millennials are paying attention to corporations environmental impact; and Millennials are interested in putting their money where their beliefs are.
These are all important factors not going unnoticed by Wall Street.
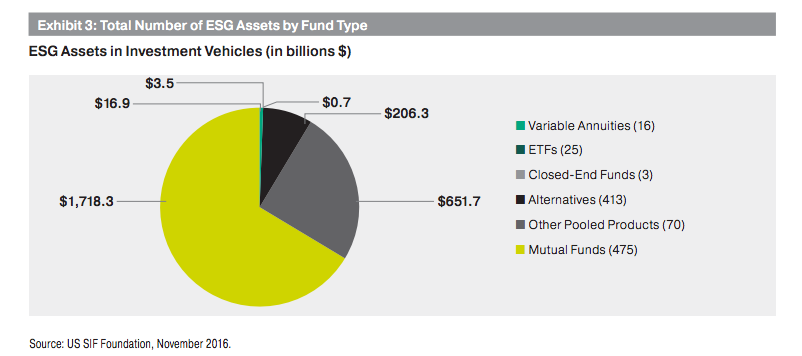
In the coming decades there will be a significant transfer of wealth. How significant? $30 trillion significant. That’s right, $30 TRILLION in wealth is estimated to pass from the Baby Boomers to their heirs, which includes Millennials. Not only do Millennials stand to benefit from this great transfer of wealth, but they are also entering the stages of their careers where they are beginning to focus on saving and investing for the future. I can attest to this, in that my WealthFusion™ program is the fastest growing segment of my business in terms of numbers of new clients.
Before long, Millennials will be controlling the majority of the economy’s wealth, and will be able to have an impact by aligning their dollars with their beliefs–which means investing with a greater purpose than wealth accumulation is here to stay, and ESG Investing will continue to grow.
A Quick Summary
To conclude this post, I want to summarize what we’ve discussed today:
- ESG investing is a philosophy that investors can not only growth their assets, but make a positive impact while doing so.
- Millennials are beginning to make their presence felt in the investment community.
- ESG Investing is becoming increasingly popular thanks to Millennials and the values they hold most important.
- Wall Street has taken notice, and more opportunities to invest with an ESG focus are available.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of ESG investing, we’re ready for the next post discussing the options individual investors have to implement ESG investing in their portfolios…
- USSIF SRI Basics: https://www.ussif.org/sribasics
- Oppenheimer Funds Undestanding ESG Investing
- American Century Investments study, highlighted in FA Magazine https://www.fa-mag.com/news/millennials-care-the-most-about-impact-investing-31506.html
Disclaimer: Nothing on this blog should be considered advice, or recommendations. If you have questions pertaining your individual situation you should consult your financial advisor. For all of the disclaimers, please see my disclaimers page.



